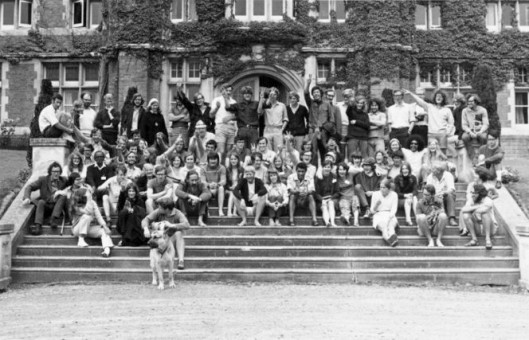This blog post was written by University of Otago history student Rachel Tombs in 2017.
“Our most important function seems to be the “air freshening”: clearing the air on the foggy, obstructive concepts of Christianity.”[1]

“The Bible in one hand, a newspaper in the other and the critic in your back pocket.” Cartoon by David Hayward and Rachel Tombs 2017. Image courtesy of SCMO.
Since the first meeting of the Otago Christian Union in 1896, its members were determined to provide a fresh approach to Christianity on campus. As descendants of the OCU, in 2017 the Student Christian Movement is focused on that same purpose. The core values; openness, education, outward vision, a foundation in Christ and the formation of student leaders, have simultaneously kept the mission of SCMO up to date and linked together Otago SCMers through the years.
Jack Bennet wrote in the NZSCM magazine “Open Windows” in 1931, “our witness must be as broadly Christian as it is possible to make it”.[2] This openness is seen throughout SCM’s history in the “free flowing” membership, and its resolution to include all people and ecumenism. [3]
Originally the only prerequisite for joining was to acknowledge Jesus Christ as saviour and to agree to abide by the constitution.[4] In the 50s as long as you felt comfortable in an “atmosphere of questioning and openness…you came along”.[5] To this day SCMO has not required a formal sign up process to attend. Aleshia Lawson describes a place where, “you can be whoever you want, I’ve never encountered any boundaries”.[6]
Through the decades SCMO has been intentional about encouraging a diversity of voices to be involved. Advertising from the 1960s proudly reads, “meet people who may or may not share your views”. [7] The first membership roll includes students from across the schools of Arts, Medicine, Mining, and Divinity.[8] The Constitution of 1896 was amended four years later to insist if the President was not a woman, the Vice President should be.[9] This policy of gender parity has since been extended to all committees and is echoed in the national and global movement.[10] The commitment to inclusion applies also to a bicultural society, demonstrated in 1993 when SCMO affirmed the national movement’s decision to incorporate the Treaty of Waitangi fully into the constitution.[11]
The primary object of the Christian Union in 1901 was to strengthen the bonds among all Christian students.[12] Initially this meant the movement was interdenominational Protestant, but by the 1970s had widened to include Roman Catholics.[13] Even before this, in the 1950s, SCMO held annual combined events with the Catholic Students’ Association. Reflecting on these events, the President wrote in 1955 “SCM is a very important field for the ecumenical encounter”.[14] SCMO continues this legacy as a current member of the Combined Christian Group.[15]
The openness of SCMO applies as much to thought as it does to people. The application of critical thought and study to faith has always been a distinguishing characteristic. Within one month of their first meeting, the executive committee set up a lending library in May 1896.[16] Study circles were also a key part of the weekly routine from this time up until the 1970s. These circles provided a place for thinking, discussion and asking questions. Russell Thew reflects that students were encouraged to “see their discipline in a much wider context.”[17] A rolling programme of guest speakers bolstered this kind of thinking. Michael Wallace describes “wanting to get into theology and really tease out some ideas.”[18] Many of these guests were local clergy or academics, but some prominent New Zealanders also left their influence on the movement, for example Ormond Burton was a keen contributor to conferences in the 1930s.[19]
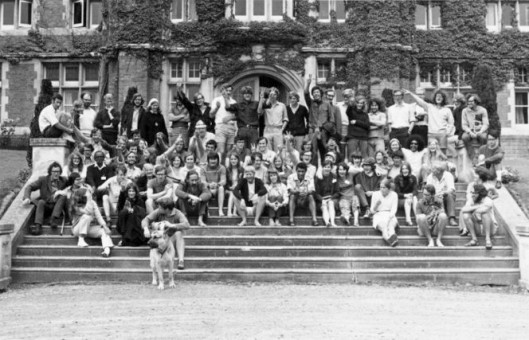
New Zealand Student Christian Movement Group gather for national conference at Knox College, ca 1970. Including James Baxter (seated left of centre) and Tim Shadbolt (back row right of centre). Image courtesy of the Alexander Turnbull Library, Wellington, Ref: PAColl-2173.
The motto adopted in 1906, “the evangelisation of the world in our generation” reflects the global aspirations of the movement. In 1896 members from the Otago Christian Union, travelled to Melbourne to attend a conference at which the Australasian Student Christian Movement was established.[20] These students were the first of many to enjoy and learn from the international connections SCMO brought. This internationalism quickly entered the discussions and activity back at home. The international friendships which developed from these conferences increased the feeling of solidarity with other countries, particularly those in the Asia- Pacific region.[21] As Peter Matheson says “there was an awareness that we weren’t just a wee blip belonging basically to Britain.”
This outward vision manifested in local activity. The Student Volunteer Movement was the dedicated branch for “mission work, especially for and by students” until the 1930s.[22] At this time the movement was split as some members felt politics and social work had ousted God and the Bible as the central purpose.[23] While the split caused the influence of the movement to wane, politics did not disappear from SCMO. After the First World War SCMers fundraised for European refugees. In 1959 they marched down George Street in Dunedin’s first anti nuclear protest.[24] Years later, during the occupations of the registry in 1993 and 1996, SCMers joined the crowds with their “God hates fees” sign and provided healthy snacks to keep energy up amongst protestors. [25] SCMO’s history is rich with campaigns like these.
Despite this activism, SCMO never strayed far from its Christian foundations. The very establishment of the Union was to enrich the lives of followers of Christ at the University. Russell Thew says that in his experience the Christian element was a major part. It was important to “take seriously the call for discipleship”.[26] Julanne Clarke-Morris recalls in the 1990s that while the group welcomed students outside the church with an interest in activism, “our constitution was very clear that we were Christian”. Although, particularly after 1930, this strand of Christianity was different to that of the conservative mainline of most churches. It was a group “prepared to be critical of its own tradition” with “a sort of impatience with traditional patterns of piety”.[27] A new member described this solid but unconventional discipleship in a 1968 newsletter, “Scmers built ungeometric and very shaky pyramids on pure faith”.[28]

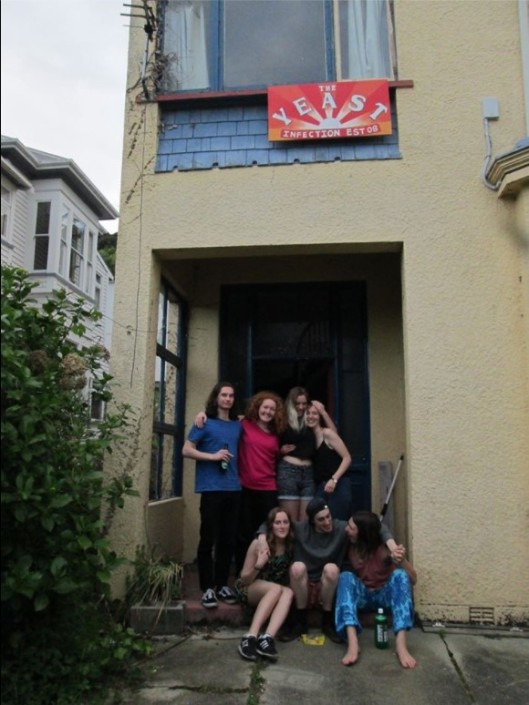
Members of SCMO attend the National Conference in 2016. Spencer Park, Christchurch. Image courtesy of SCMA.
The same fresher added “scmers never stayed still or silent for long.” SCMO formed students into competent, confident and active leaders. It was a place where students were encouraged to think for themselves and develop into “adult Christians”.[29] In the 1950s one of the movement’s objectives was to earn members “the right to dissent”. [30] Julanne Clarke Morris echoes this “if it wasn’t for SCM I wouldn’t have that sort of confidence in my own interpretation.”
Student movements tend to be places where distinctive common characteristics are held.[31] In the case of SCMO the core values distinguish it from other student and Christian groups. SCMO does not wish to be church in a traditional sense, but could never be considered simply “a youth group”.[32] It is the interaction of these values: openness to people and thought, internationalism and social justice, student leadership, all with Christ at the centre, which combined together smell like the air freshener that is SCMO, throughout its 121 years.
Bibliography:
Berry, Christine. The New Zealand Student Christian Movement 1896-1996: A Centennial History. Christchurch.: NZ, SCMA, 1999.
Lineham, Peter. “Finding a space for evangelicalism: Evangelical Youth Movements in New Zealand”, in Voluntary religion: papers read at the 1985 Summer Meeting and the 1986 Winter Meeting of the Ecclesiastical History Society, ed.W. J Sheils and Diana Wood. Oxford, UK.: Blackwell, 1986.
Otago University Student Christian Movement Records 1896-1973 (90-138, boxes 1-5) Hocken Archives Dunedin.
Interviews:
Peter Matheson, involved late 1950s and 1981- 2017, interview by the author, Dunedin New Zealand, 20th September 2017.
Russell Thew, involved 1966-1973, interview by the author, Dunedin New Zealand, 20th September, 2017.
Julanne Clarke-Morris, involved 1990 -1997, interview by the author, Dunedin New Zealand, 27th September 2017.
Michael Wallace, involved 1989-2017, interview by the author, Dunedin New Zealand, 27th September 2017.
Aleshia Lawson, involved 2013-2017, interview by the author, Dunedin New Zealand, 29th September 2017.
John Graveston, involved 2013-2017, interview by the author, Dunedin New Zealand, 29th September 2017.
Endnotes:
[1] Geoff and Helen White, “A New Fundamentalism” for the SCMO Newsletter, ca. 1968, Student Christian Movement, 90-138, box 4, Hocken Collections Dunedin.
[2] Open Windows, vol.5 no. 2, April 1931, in The New Zealand Student Christian Movement 1896-1996: A Centennial History, Christine Berry (Christchurch.: NZ, SCMA, 1999), 1:8.
[3] Peter Matheson, interview by the author, Dunedin New Zealand, 20th September 2017. Involvement late 1950s, 1981 – 2017.
[4] Minute Book for the Executive Committee, 1896 -1910, Student Christian Movement, 90-138, box 1, Hocken Collections Dunedin.
[5] Peter Matheson
[6] Aleshia Lawson, interview by the author, Dunedin New Zealand, 29th September, 2017. Involvement 2013-2017.
[7] SCMO Newsletters 1958-1972, Student Christian Movement, 90-138, box 4, Hocken Collections Dunedin.
[8] Record Book Otago Christian Union, 1896 -1904, Student Christian Movement, 90-138, box 3, Hocken Collections Dunedin.
[9] Minute Book for the executive committee, 1896-1910.
[10] John Graveston, interview by author, Dunedin New Zealand, 29th September 2017. Involvement 2013-2017.
[11] Berry, appendix 2.
[12] Record Book Otago Christian Union, 1896 -1904.
[13] Michael Wallace, interview by author, 27th September 2017. Involvement 1989-2017.
[14] Presidents Book 1955-1972, Student Christian Movement, 90-138, box 2, Hocken Collections Dunedin.
[15] John Graveston
[16] Minute Book of the Executive Committee 1896-1910.
[17] Russell Thew, interview by author, Dunedin New Zealand, 20th September 2017. Involvement 1966-1973.
[18] Michael Wallace
[19] Julanne Clarke-Morris, interview by author, Dunedin New Zealand, 27th September 2017. Involvement 1990-1997. Berry, 2:4.
[20] Minute Book of the Executive Committee 1896 -1910.
[21] Julanne Clarke-Morris, interview by author, Dunedin New Zealand, 27th September.
[22] Record Book, 1896-1904.
[23] Berry, 2:6-9. Peter Lineham, “Finding a space for evangelicalism: Evangelical Youth Movements in New Zealand”, in Voluntary religion: papers read at the 1985 Summer Meeting and the 1986 Winter Meeting of the Ecclesiastical History Society, ed.W. J Sheils and Diana Wood (Oxford, UK.: Blackwell, 1986), 485.
[24] Peter Matheson
[25] Julanne Clarke-Morris
[26] Russell Thew
[27] Julanne Clarke Morris. Lineham, 483. Peter Matheson.
[28] SCMO Newsletters 1958-1972
[29] Michael Wallace
[30] SCMO Newsletters 1958-1972
[31] Lineham, 477.
[32] Julanne Clarke-Morris
Note: Ian Dougherty’s ‘Whatever happened to the Student Christian Movement?’ in the University of Otago Magazine, 46, April 2018, drew on the unpublished work that Rachel completed for this blog in 2017.