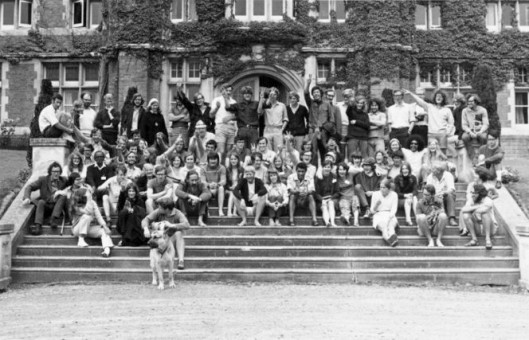Tags
This post was researched and written by University of Otago history student Bree Wooller in 2017.

86 Queen Street 2016. Photographed by Bree Wooller.
North Dunedin has not always been occupied by students. For most of its history it has been just another suburb. Now, the houses are crumbling, and we risk losing the heritage and character that has become iconic to the area.
The gold rush of the 1860s made Dunedin the richest and most highly populated province in New Zealand.[1] This influx of wealth influenced the building of large, elegant, houses along the town belt. In 1880, David Henderson built a house at 86 Queen Street. In its early years 86 Queen was considered a charming, first-class, modern residence.[2] The early occupants were wealthy; regular adverts posted in the local papers look for domestic help, and furniture auctions reveal the occupants lavish lifestyle.[3] Walnut pianos, marble vases, and oil paintings were common furnishings in 86 Queen Street at the time.[4]

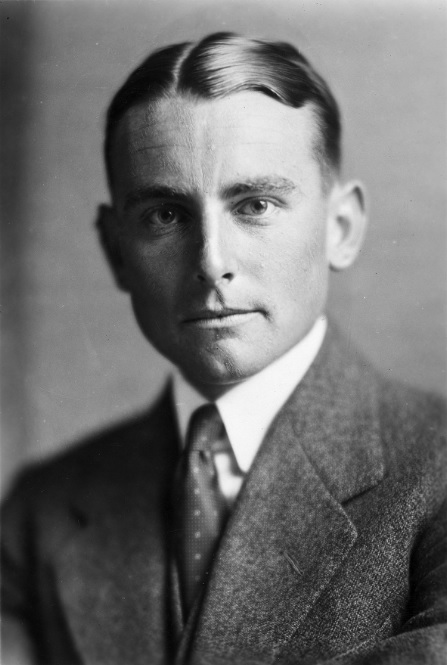
Professor Salmond had a brief occupancy till his death in 1917. Photographed by Morris, 1914. Image courtesy of Hocken Collections, P2018-013-005.
John Laing, a ‘foreign agent,’ owned the house from 1909 to 1924. He lived there with his wife Kathleen, son John Carroll, and daughter Katherine.[5] John Carroll Laing was killed in action in Italy, 1943.[6] Professor William Salmond, known for his position on the chair of mental and moral philosophy at Otago University, appears to have resided at the house for a brief amount of time up until his death in 1917.[7] Kathleen Laing’s brother, Dr Francis Hotop, a surgeon at Dunedin Hospital lived with the family for a period around 1922.[8] Their father, Lewis Hotop, a pharmacist and three-time Mayor of Queenstown, was also living at the residence until his death in 1922.[9]

House Interior 2016. Contrast of modern repairs and older features in balusters and stained window panes. Photographed by Bree Wooller, July 2016.
A new upstairs room was added in 1913, electricity was connected during the renovations.[10] In 1926, a garage was added at the front of the house.[11]
90 years ago, Dunedin was feeling the effects of the Great Depression.[12] Large houses along the town belt became too hard to maintain during this economic downturn, most were split into multiple dwellings. In the late 1930s, 86 Queen Street was split into a top and bottom flat.[13]
The house was rented in this period by a fast-changing array of occupants. Tenants included Miss Anna Glover, a spinster, who lived in the top flat 1940 to 1946, and an engineer named David Jack, who lived in the bottom flat from 1939-41.[14] The flat was owned by a retired salesman, Thomas McGoldrick, from 1944 till his death in 1969.[15] In 1958, the iconic yellow roughcasting replaced the houses traditional wooden exterior, making it resemble its present-day appearance.
Between 1969 and 1979, 86 Queen Street was owned and occupied by Richard Mulgan and his wife Margaret.[16] Mulgan was a professor of political studies at Otago University, known for his role on the New Zealand Royal Commission of 1985, which recommended the adoption of an MMP political system. Mulgan converted 86 Queen back to a single house, and remodelled the kitchen in 1976. From 1979, the flat was owned and occupied by Duncan Roper and his wife Mirrel.[17] Duncan was a tutor at the university while residing in the house.
50 years ago, the university roll was on a steady climb, and the number of students wanting to flat was on the rise.[18] In 1956, 17% of the student population lived in flats, and this rose to 39% of students in 1972.[19]

Student Occupation at 86 Queen Street. Photographed by Bree Wooller, October 2016.
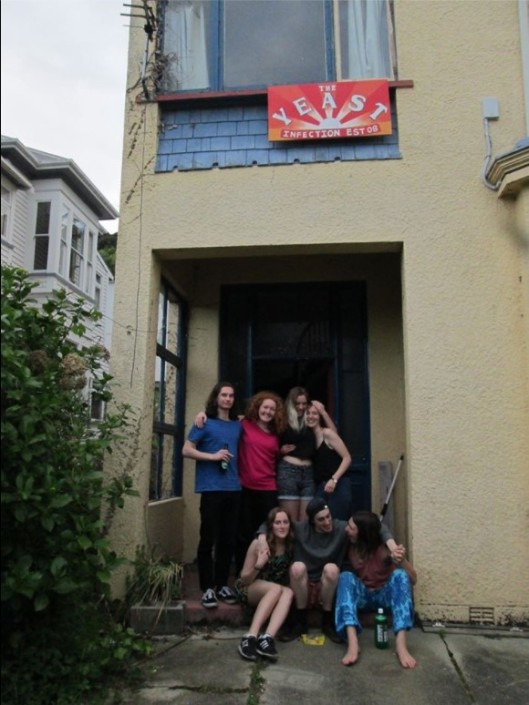
The beginning of student occupation at 86 Queen Street is ambiguous. Names and dates in an upstairs room suggest students were living in the flat from 2001, if not earlier. 86 Queen Street became known as “The Yeast Infection” in 2008.
In 2017, we face the continued issue of degrading student flats. Maintenance and care is needed to preserve old houses such as 86 Queen Street. Without this, many historic flats will be demolished. Along with them, aspects of student culture, and landmarks of the first settler’s Dunedin will be lost forever.
Notes
[1] Erik Olssen, A History of Otago (Dunedin, N.Z. : McIndoe,1984), 69.
[2] Park, Reynolds and Co, “Charming City Residence and Choice Piece of Ground” Evening Star (Issue: 11528), 20th April 1901.
[3] Gow, “Wanted, Respectful General Servant”, Evening Star (Issue 11411), 1 December 1900.; Mrs Laing “Wanted, Young Lady”, Evening Star (Issue: 14150), 30th October 1913.; Mrs George Mackie, “Wanted, Young Girl” Otago Daily Times (Issue: 19225), 16th July 1924.
[4] Park, Reynolds and Co, “Superior Household Furniture”, Evening Star (Issue: 11528), 20th April 1901.
[5] Laing, “Birth Notices”, Otago Witness (Issue 3060), 6th November 1912; Wise’s New Zealand Post Office Directory, 1909-1924.
[6] Northern Cemetery, block 191, plot 86, 85. New Zealand, Cemetery Records, 1800-2007. Ancestry.com.
[7] “Auctions – Estate of the Late Professor Salmond” Evening Star (Issue 16422), 12th May 1917.; Wise’s New Zealand Post Office Directory, 1917.
[8] Dr F. R. Hotop, “Professional Advertisement – Commenced Practice”, Otago Daily Times (Issue 18518), 31st March 1922.
[9] Hotop “Death Notice”, Otago Daily Times, (Issue 18673), 30th September 1922.
[10] Electricity Records, 3rd July 1913. Register No. 3329. Dunedin City Council Archives.
[11] Building Plans, 1926. No. 8788. Dunedin City Council Archives.
[12] Olssen, 90.
[13] Electricity Records, 24th June 1940. Register No. 32313. Dunedin City Council Archives.
[14] Wise’s New Zealand Post Office Directory, 1940, 1942, 1943, 1946.; Electricity Records Register No. 32313.
[15] Anderson Bay Cemetery, block 259, plot 27. New Zealand, Cemetery Records, 1800-2007. Ancestry.com; Electricity Records Register No. 32313; Wise’s New Zealand Post Office Directory, 1947, 1950-1, 1953-4, 1955.
[16] Dunedin, Otago, 1978. New Zealand Electoral Rolls, 1853–1981. Auckland, New Zealand: BAB microfilming. Microfiche publication, 4032 fiche. Ancestry.com.
[17] Dunedin, Otago, 1981. New Zealand Electoral Rolls, 1853–1981.
[18] Debby Foster “No Mixing By Students” in Tower Turmoil: Characters and Controversies at the University of Otago, ed. Time Keepers. (Dunedin: Department of History, University of Otago, 2005) 129
[19] Sam Elworthy, Ritual Song of Defiance: A Social History of Students at the University of Otago, (Dunedin: OUSA, 1990), 199.
Bibliography
Auckland Museum Online Cenotaph. J C Laing. Record: C28301, Service Number: 600485.
Building Plans, No. 8788. Dunedin City Council Archives.
Evening Star. Dunedin, New Zealand, 1 December 1900 – 12 May 1917.
Electricity Records, 3rd July 1913. Register No. 3329. Dunedin City Council Archives.
Electricity Records, 24th June 1940. Register No. 32313. Dunedin City Council Archives.
Elworthy, Sam. Ritual Song of Defiance: A Social History of Students at the University of Otago. Dunedin: OUSA. 1990.
Foster, Debby. “No Mixing By Students.” In Tower Turmoil: Characters and Controversies at the University of Otago, edited by Time Keepers. Dunedin: Department of History, University of Otago. 2005.
McLeod, Catherine. “Halls of residence in the 1960s: curfews, couples and controversy.” In Tower Turmoil: Characters and Controversies at the University of Otago, edited by Time Keepers. Dunedin: Department of History, University of Otago. 2005.
New Zealand Electoral Rolls, 1853–1981. Auckland, New Zealand: BAB microfilming. Microfiche publication, 4032 fiche. Ancestry.com.
New Zealand, Cemetery Records, 1800-2007. Ancestry.com.
Olssen, Erik. A History of Otago. Dunedin: McIndoe, 1984.
Otago Daily Times. Dunedin, New Zealand, 31 March 1922 – 16 July 1924.
Otago Witness, Dunedin, New Zealand, 17 March 1898.- 6 November 1912.
Professor W. Salmond, by Morris Phot, 1914. Hocken Collections (c/nF189/1)
Wise’s New Zealand Post Office Directory, 1898-1955. New Zealand, City & Area Directories, 1866-1955. Microfilm publication, 921 fiche. Anne Bromell Collection. Ancestry.com.